How To Change A Quadratic Equation To Standard Form
Standard Course of Quadratic Equation
The standard grade of quadratic equation is axii + bx + c = 0, where 'a' is the leading coefficient and information technology is a non-zero real number. This equation is called 'quadratic' as its degree is 2 because 'quad' means 'square'. Apart from the standard form of quadratic equation, a quadratic equation can be written in other forms.
- Vertex Grade: a (x - h)2 + k = 0
- Intercept Class: a (ten - p)(ten - q) = 0
Let u.s.a. learn more about the standard form of a quadratic equation and let u.s.a. run across how to convert one grade of a quadratic equation into another.
| ane. | What is the Standard Course of Quadratic Equation? |
| 2. | Converting Standard Grade of Quadratic Equation into Vertex Form |
| 3. | Converting Standard Grade of Quadratic Equation into Intercept Course |
| 4. | FAQs on Standard Form of Quadratic Equation |
What is the Standard Form of Quadratic Equation?
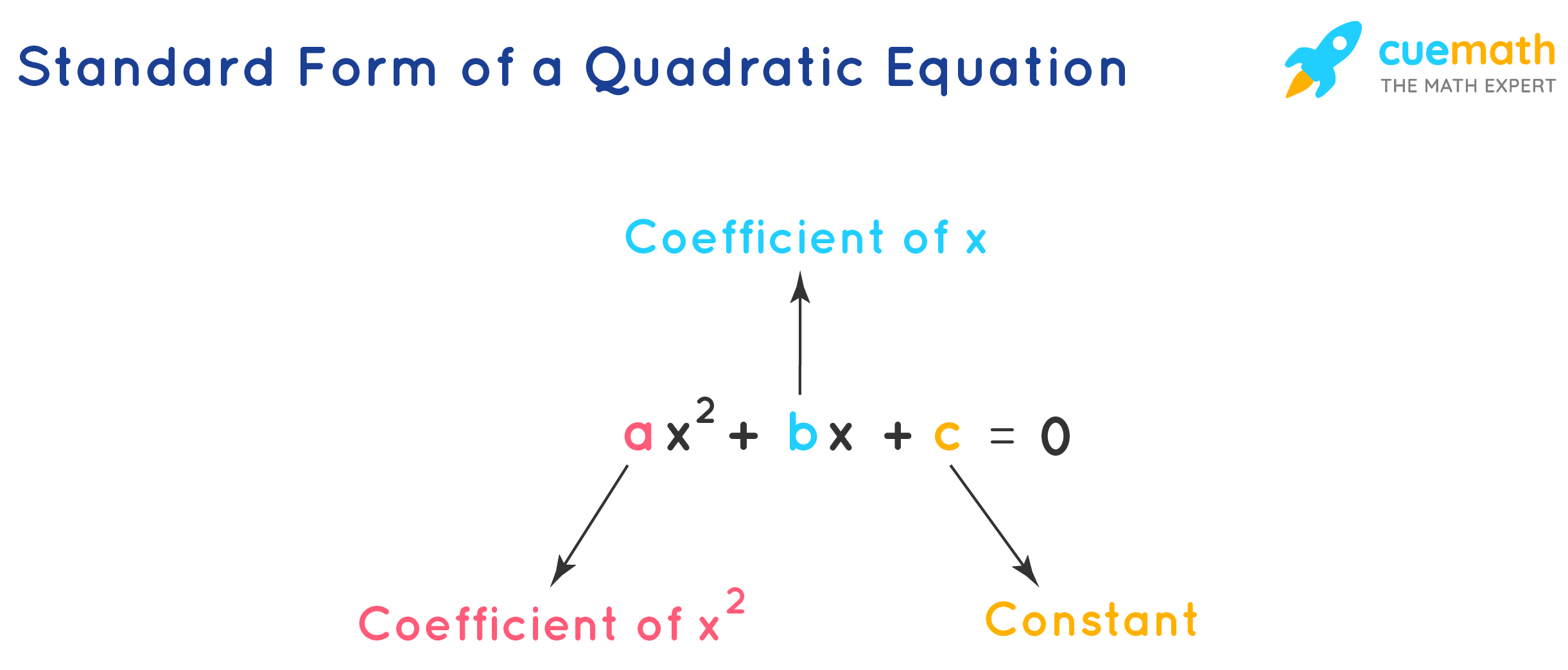
The standard form of quadratic equation with a variable x is of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0, and a, b, and c are existent numbers. Here, b and c tin can be either zeros or non-zero numbers and
- 'a' is the coefficient of x2
- 'b' is the coefficient of ten
- 'c' is the constant
Examples of Standard Form of Quadratic Equation
Here are some examples of quadratic equation in standard class.
- 2x2 - 7x + viii = 0
- (-one/3) x2 + 2x - ane = 0
- x2 - 8 = 0
- -3x2 + 8x = 0
General Form of Quadratic Equation
The standard form of a quadratic equation is also known as its full general form. Thus, the general course of a quadratic equation is also axtwo + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0.
Converting Standard Course of Quadratic Equation into Vertex Course
Allow u.s. convert the standard form of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 into the vertex grade a (10 - h)2 + grand = 0 (where (h, yard) is the vertex of the quadratic role f(x) = a (x - h)two + k). Note that the value of 'a' is the same in both the equations. Allow us just gear up them equal to know the relation betwixt the variables.
axii + bx + c = a (x - h)two + thou
axtwo + bx + c = a (x2 - 2xh + h2) + k
axii + bx + c = axtwo - 2ah ten + (ah2 + k)
Comparing the coefficients of x on both sides,
b = -2ah ⇒ h = -b/2a ... (i)
Comparing the constants on both sides,
c = ahii + k
c = a (-b/2a)2 + k (From (1))
c = btwo/(4a) + thousand
k = c - (b2/4a)
thou = (4ac - b2) / (4a)
Thus, we can use the formulas h = -b/2a and grand = (4ac - bii) / (4a) to convert standard to vertex course.
Instance of Converting Standard Form to Vertex Form
Consider the quadratic equation 2x2 - 4x + 3 = 0. Comparing this with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get a = 2, b = -4, and c = 3. To convert it into the vertex form, let us find the values of h and yard.
- h = -b/2a = -(-4) / (2 · two) = 1
- k = (4ac - b2) / (4a) = (4 · 2 · iii - (-4)2) / (iv · two) = (24 - 16) / 8 = 1
Substituting a = 2, h = i, and k = ane in the vertex form a (ten - h)2 + g = 0, nosotros get:
2 (x - ane)ii + 1 = 0
Converting Vertex Form to Standard Course
The process of converting the vertex grade of a quadratic equation into the standard form is pretty unproblematic and it is washed by simply evaluating (ten - h)ii = (x - h) (x - h) and simplifying. Let us consider the above instance ii (x - 1)two + one = 0 and let usa convert it back into standard form.
2 (x - i)two + ane = 0 -------> Vertex Class
2 (10 - ane) (10 - one) + 1 = 0
2 (tentwo - x - 10 + ane) + 1 = 0
ii (x2 - 2x + 1) + 1 = 0
2x2 - 4x + ii + 1 = 0
2x2 - 4x + 3 = 0 --------> Standard Form
Converting Standard Form of Quadratic Equation into Intercept Grade
Let usa convert the standard course of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 into the vertex course a (x - p)(10 - q) = 0. Here, (p, 0) and (q, 0) are the x-intercepts of the quadratic function f(10) = ax2 + bx + c) and hence p and q are the roots of the quadratic equation. Thus, nosotros just use any ane of the solving quadratic equation techniques to discover p and q.
Case to Convert Standard to Intercept Form
Consider the quadratic equation 2xtwo - 7x + 5 = 0. By comparing this with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we go a = two. Now nosotros will solve the quadratic equation by factorization.
2x2 - 7x + five = 0
2x2 - 2x - 5x + five = 0
2x (10 - 1) - 5 (10 - one) = 0
(x - one) (2x - 5) = 0
x - one = 0; 2x - 5 =0
ten = 1; x = 5/two
Thus, p = 1 and q = five/2
Thus, the intercept course is,
a (x - p)(x - q) = 0
ii (x - 1) (10 - v/2) = 0
ii (10 - one) (2x - 5)/2 = 0
(x - 1) (2x - 5) = 0
Converting Intercept Form to Standard Course
The process of converting the intercept course of a quadratic equation into standard form is actually easy and information technology is done by merely multiplying the binomials (x - p) (x - q) and simplifying. Let the states consider the to a higher place case (x - 1) (2x - 5) = 0 and let us convert information technology back into standard class.
(x - i) (2x - 5) = 0 -------> Intercept Form
2x2 - 5x - 2x + v = 0
2x2 - 7x + 5 = 0 --------> Standard Form
Important Notes on Standard Course of Quadratic Equation:
- A quadratic equation in standard form is ax2 + bx + c = 0.
- A quadratic equation in vertex form is a (x - h)2 + yard = 0.
- A quadratic equation in intercept form is a (10 - p)(x - q) + k = 0.
☛Related Topics
- Quadratic Expressions
- Multiplying Binomials Calculator
- Quadratic Equation Computer
- Roots of Quadratic Equation Calculator
Examples of Quadratic Equation in Standard Course
go to slidego to slidego to slide

Have questions on basic mathematical concepts?
Become a trouble-solving champ using logic, not rules. Acquire the why backside math with our certified experts
Book a Gratuitous Trial Class
Practise Questions on Standard Course of Quadratic Equation
become to slidego to slide
FAQs on Standard Form of Quadratic Equation
What is the Standard Form of Quadratic Equation?
The standard grade of a quadratic equation with variable x is expressed as ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a,b, and c are constants such that 'a' is a non-cypher number only the values of 'b' and 'c' tin exist zeros.
Tin 'c ' exist a Zero in the Standard Class of Quadratic Equation?
In the standard form of quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, just 'a' has a restriction that it should not be a zero. So the value of 'c' can be 0.
What is an Example of Quadratic Equation in Standard Grade?
Some examples of quadratic equations in standard class are:
- 3x2 - 7x + two = 0
- ten2 - 4x + (1/2) = 0
- 5x2 - 20 = 0
- 102 + 10 = 0
How to Convert a Quadratic Equation From Standard to Vertex Form?
The standard form of a quadratic equation is axtwo + bx + c = 0. To convert it into the vertex form a(x - h)2 + k = 0,
- The value of 'a' is obtained from the standard grade.
- h = -b/2a
- k = (4ac - b2) / (4a)
Can 'a' be a Zippo in Standard Class of Quadratic Equation?
The standard form of quadratic equation is ax2 + bx + c = 0. If a = 0, then the equation becomes bx + c = 0 which is not quadratic anymore. Thus, the value of 'a' should Not be a zero in a quadratic equation.
What is the Divergence Between the Full general Course of Quadratic Equation and the Standard Grade of Quadratic Equation?
The standard form of a quadratic equation is equally same as its full general course and is expressed as ax2 + bx + c = 0 where 'a' is not-zero.
Can 'b' be a Naught in the Standard Form of a Quadratic Equation?
In the standard form of quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, merely 'a' shouldn't be a nada. And so the value of 'b' can be 0.
Source: https://www.cuemath.com/algebra/standard-form-of-quadratic-equation/#:~:text=The%20process%20of%20converting%20the,x%20%2D%20h)%20and%20simplifying.
Posted by: fleisherboulciance1971.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Change A Quadratic Equation To Standard Form"
Post a Comment